As a fun exercise, I decided to create an SSIS package & then replicate the functionality using Python for a PostgreSQL database. I had a lot of fun with this. While the packages perform fairly simple operations, there were some interesting aspects.
Overview:
- Create a new table based on an existing table
- Add a field to the table to hold concatenated data from existing fields
- Truncate the table
- Create a CSV file from a query of the original table
- Create the mechanism that will modify the data (SSIS package/Python function), populating the new field
- Load the data into the new table
Notes:
- I found a very helpful blog post that covers using nested conditional operators in an SSIS derived column.
- I used the Person.Person table in the AdventureWorks2014 database in both environments.
- The derived column consists of the FirstName, MiddleName & LastName fields, with appropriate handling for NULL or empty values & appropriate spacing.
- The Person.Person table has XML & UniqueIdentifier fields that proved a little tricky in the import step in SSIS. They were skipped (and will become a future blog post). The same fields were not a problem for the Postgres import.
Process:
Table & Data Creation – SQL Server
--1) Create a new table based off of Person.Person --SELECT TOP(10) * --INTO dbo.XPerson --FROM PERSON.PERSON --2) Alter new table, adding FullName field --ALTER TABLE dbo.XPerson --ADD FullName NVARCHAR(152) NULL --3) Truncate Table --TRUNCATE TABLE dbo.XPerson --4) Save the results of this query to a CSV file SELECT TOP(10) * FROM PERSON.Person p
Table & Data Creation – PostgreSQL
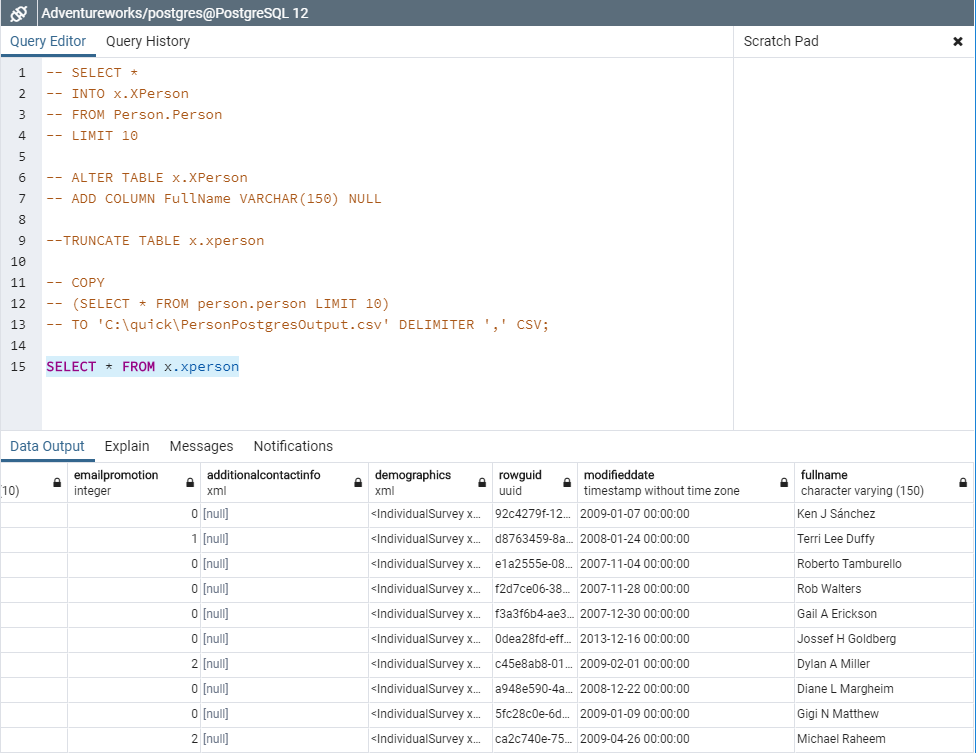
--1) Create a new table based off of Person.Person -- SELECT * -- INTO x.XPerson -- FROM Person.Person -- LIMIT 10 --2) Alter new table, adding FullName field -- ALTER TABLE x.XPerson -- ADD COLUMN FullName VARCHAR(150) NULL --3) Truncate Table --TRUNCATE TABLE x.xperson --4) The following creates the CSV input file -- COPY -- (SELECT * FROM person.person LIMIT 10) -- TO 'C:\quick\PersonPostgresOutput.csv' DELIMITER ',' CSV;
I want to award a point to Postgres for making the CSV file creation so easy. While there is the “Results to File” option in SSMS, I really like the Postgres handling.
SSIS Package:
The SSIS package consisted of the:
- Connection Manager for the CSV file
- Connection Manager to the Database
- Data Flow with a:
- Flat File Source
- Derived Column
- OLE DB Destination
The expression for the derived column:
[Column 4] + " " + ([Column 5] != "NULL" ? [Column 5] + " " : "") + [Column 6]
As seen in the screenshot below, there was a problem with the package.
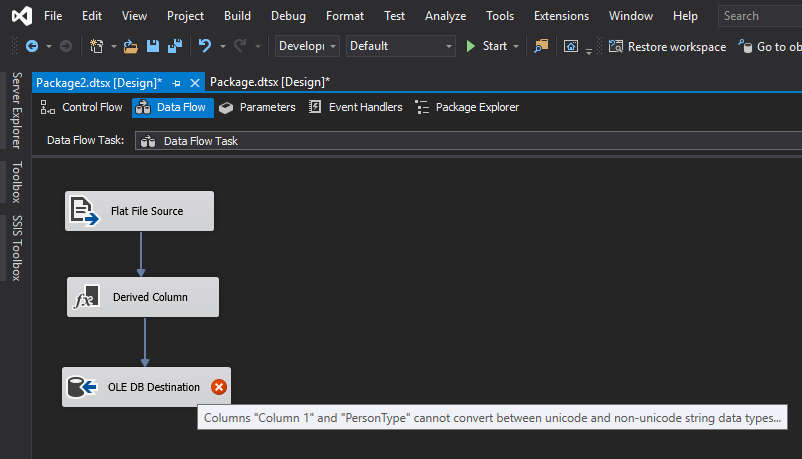
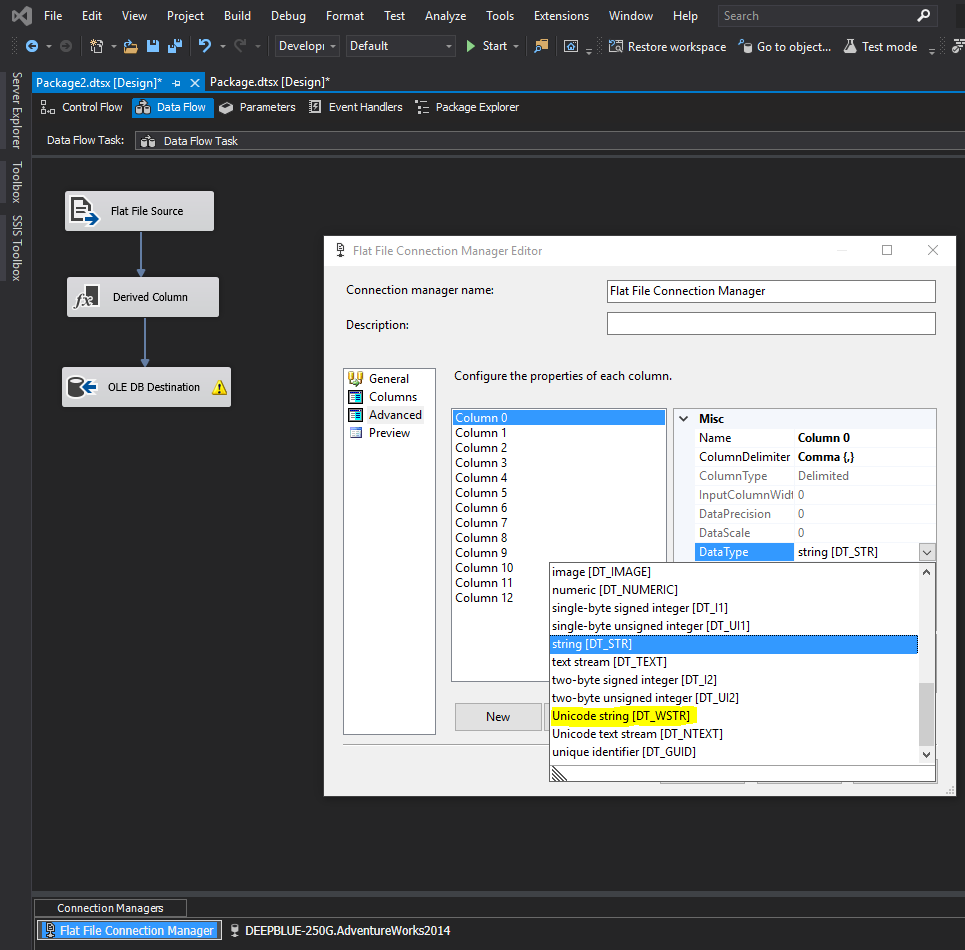
By default, the columns had a DataType of DT_STR. Converting them to DT_WSTR resolved the error (see below).
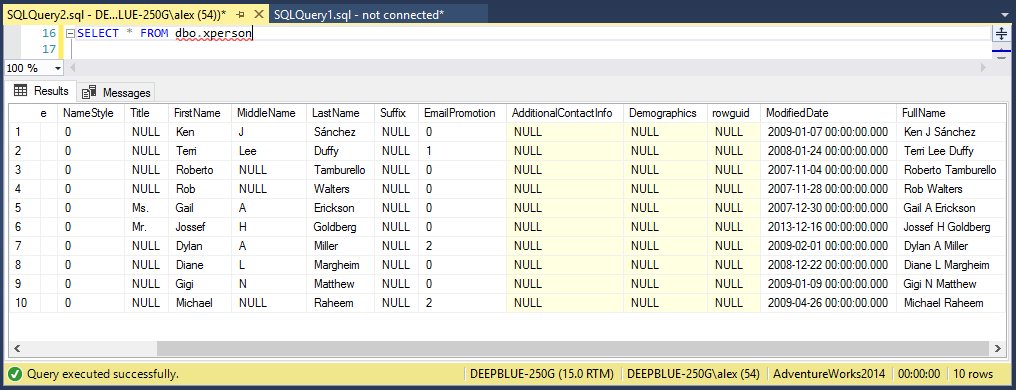
The package ran successfully, resulting in the output below.
Python/PostgreSQL:
The corresponding Python code came down to 2 blocks of code; one to modify the data & the other to write the data to the table.
import csv
original_file = open('C:\quick\PersonPostgresOutput.csv', 'r')
original_file_reader = csv.reader(original_file)
original_file_reader_list = list(original_file_reader)
first_name_column = 4
middle_name_column = 5
last_name_column = 6
for row in range(len(original_file_reader_list)):
original_file_reader_list[row].append(
original_file_reader_list[row][first_name_column] + " "
+ (original_file_reader_list[row][middle_name_column] + " "
if (original_file_reader_list[row][middle_name_column] != 'NULL'
and original_file_reader_list[row][middle_name_column] != '') else '')
+ original_file_reader_list[row][last_name_column]
)
updated_file = open('c:\quick\PersonPostgresOutput_Updated.csv', 'w', newline='')
updated_file_writer = csv.writer(updated_file, delimiter=',')
for row in range(len(original_file_reader_list)):
updated_file_writer.writerow(original_file_reader_list[row])
updated_file.close()
import psycopg2
with psycopg2.connect(user='postgres', password='mnbvcx', database='Adventureworks', host='localhost') as connection:
with connection.cursor() as cursor:
cursor.execute("COPY x.xperson FROM 'C:\quick\PersonPostgresOutput_Updated.csv' DELIMITERS ',' CSV;")
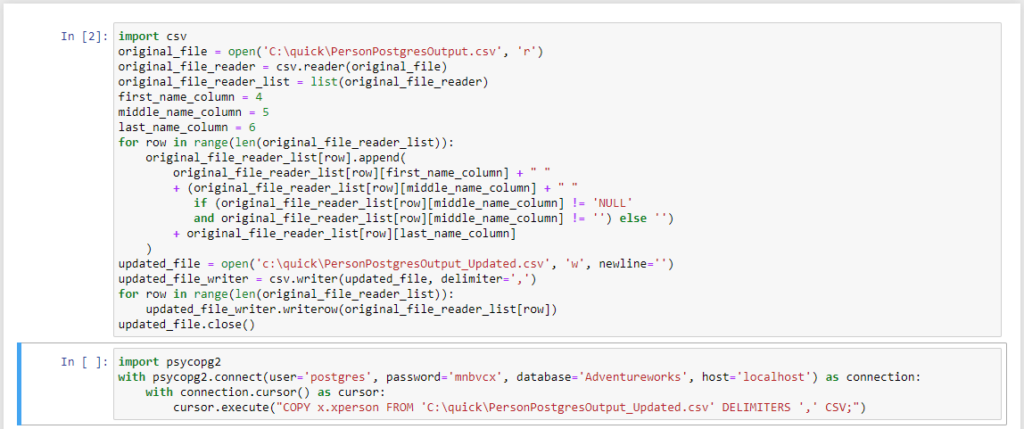
The code ran successfully. The XML & UUID fields weren’t an issue and no datatype conversions were necessary. The results can be seen below.
Closing:
- As previously stated, this was a lot of fun.
- Compared to my exposure to the SQL Server, it is still early days with Python & Postgres. If you have thoughts, tips, tricks, corrections, etc., please leave a comment below.
- If you have an questions, please feel free to ask in the comments & I will be happy to follow up.